Dell Streak 7 taken apart already? Yeah, we went there. This isn’t your average tech teardown; this is a deep dive into the guts of a forgotten legend, the Dell Streak 7. We’re talking physical components, meticulous disassembly, component identification, and even a peek at its repair quirks. Prepare for a nostalgic trip down memory lane, complete with unexpected discoveries and maybe a few “aha!” moments.
From the delicate dance of removing the back cover to the intricate web of internal connections, we’ll chronicle every step of the process. We’ll analyze its components, compare it to its contemporaries, and uncover the secrets behind its design choices. Think of it as an autopsy of a tech relic, revealing its strengths, weaknesses, and the overall engineering that made (or broke) this little tablet.
Dell Streak 7 Physical Components
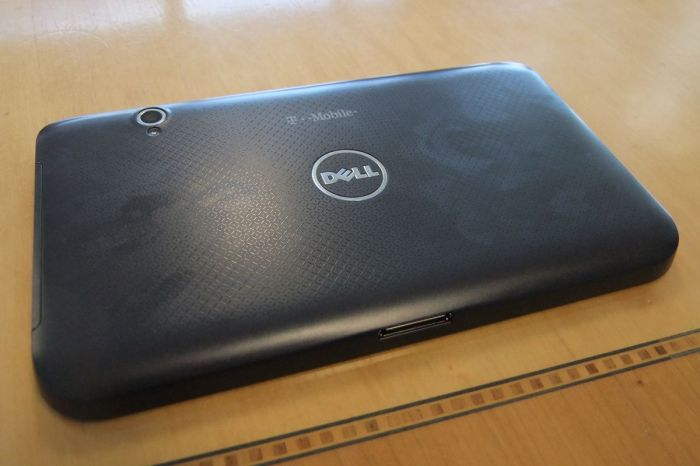

Taking a Dell Streak 7 apart reveals a surprisingly intricate arrangement of components, a testament to the miniaturization of technology in the early 2010s. This peek inside offers a fascinating glimpse into the physical construction of this pioneering tablet. Let’s explore the individual parts and their roles.
Internal Component Breakdown
The Dell Streak 7’s internal structure is a delicate dance of circuit boards, batteries, and screens carefully nestled together. Understanding these components and their arrangement is key to appreciating the device’s design and functionality.
| Component | Material | Size (approximate) | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motherboard | Printed Circuit Board (PCB) | 70mm x 50mm | Central processing unit, housing the CPU, GPU, RAM, and other key integrated circuits. |
| LCD Screen | Glass, LCD panel, backlight | 7 inches diagonal | Displays visual information to the user. |
| Battery | Lithium-ion polymer | 60mm x 40mm x 10mm | Provides power to the device. |
| Touchscreen Digitizer | Glass, conductive layers | 7 inches diagonal | Translates touch inputs into digital signals. |
| Front-Facing Camera | Plastic, lens, sensor | 10mm diameter | Captures images and videos for video calls and selfies. |
| Rear-Facing Camera | Plastic, lens, sensor | 15mm diameter | Captures images and videos. |
| Various Connectors | Plastic, metal | Varying | Enable connection to external devices (e.g., charging port, headphone jack). |
| Speaker | Plastic, speaker element | 20mm x 10mm | Produces audio output. |
| Vibrator | Ceramic, motor | 15mm x 5mm | Provides haptic feedback. |
Battery Specifications and Physical Description, Dell streak 7 taken apart already
The Dell Streak 7 utilizes a Lithium-ion polymer battery. This type of battery is known for its high energy density and relatively lightweight nature, making it suitable for portable devices. While the exact capacity may vary slightly depending on the manufacturing batch, a typical Dell Streak 7 battery holds approximately 4000 mAh (milliampere-hours). Physically, it’s a relatively flat, rectangular cell, approximately 60mm long, 40mm wide, and 10mm thick. Its location is typically towards the back of the device, near the bottom edge, often adhered directly to the back casing.
Internal Layout Illustration
Imagine the Dell Streak 7 laid flat, screen facing up. The LCD screen and touchscreen digitizer are the topmost layers. Below this lies the motherboard, centrally located, occupying a significant portion of the internal space. The battery is usually positioned towards the bottom, adhered to the back casing. The cameras are located at the top and back of the device, their lenses poking through carefully placed openings in the casing. Connectors are situated along the edges, often near the bottom for charging and data transfer. The speaker and vibrator are typically embedded within the device casing. All these components are interconnected through a network of cables and connectors, forming a complex but efficient system. The entire assembly is enclosed within a plastic casing for protection.
Disassembly Procedure and Steps
Taking apart a Dell Streak 7 requires patience and a steady hand. This process isn’t for the faint of heart, but with the right tools and a methodical approach, you can successfully disassemble this early Android tablet. Remember, this process voids any warranty, so proceed with caution.
The following steps detail the complete disassembly of a Dell Streak 7, from removing the back cover to separating the internal components. Accurate identification of each component is crucial before disconnecting any connectors or removing screws. Take your time, and refer to images or diagrams if needed for visual assistance. Misidentification can lead to irreparable damage.
Tools Required for Disassembly
Before beginning, gather the necessary tools. Improper tools can easily damage the delicate components within the device. A complete toolkit ensures a smooth disassembly process. These tools will make the process significantly easier and safer.
- Small Phillips head screwdriver (preferably magnetic-tipped for easier screw handling)
- Spudger or plastic opening tool (to avoid scratching the device’s casing)
- Tweezers (for handling small components)
- Anti-static wrist strap (to prevent electrostatic discharge damage to sensitive electronics)
- A well-lit workspace with sufficient room to lay out components in an organized manner
Step-by-Step Disassembly Process
The disassembly process involves several steps, each requiring careful attention to detail. Improper handling can result in broken connectors or damaged components. Follow these steps sequentially to ensure a successful disassembly.
- Remove the Back Cover: Using a spudger or plastic opening tool, carefully pry open the back cover. Start at a corner and gently work your way around the perimeter. The adhesive holding the back cover may be strong, so apply even pressure to avoid cracking the plastic.
- Disconnect the Battery Connector: Once the back cover is removed, locate the battery connector. Using a spudger, carefully disconnect the connector from the motherboard. This is a crucial step to prevent short circuits.
- Remove the Battery: After disconnecting the connector, carefully remove the battery. It might be adhered to the chassis with adhesive. Gently pry it loose using a spudger, taking care not to damage the battery cells.
- Remove Screws and Internal Components: Several screws secure the motherboard and other internal components. Carefully remove these screws using the Phillips head screwdriver, keeping track of their locations and lengths for reassembly. Once the screws are removed, carefully lift and separate the motherboard from the chassis. Pay attention to ribbon cables connecting the display and other components.
- Disconnect Ribbon Cables: Use a spudger to gently disconnect the ribbon cables connecting the display, touch screen, and other components to the motherboard. Be very careful not to bend or damage these delicate connectors. Note the orientation of each connector before disconnecting.
- Separate Remaining Components: Once all connectors are disconnected, carefully separate the remaining components, such as the camera module, speakers, and other smaller parts. Use tweezers to handle smaller components to avoid damage.
Potential Difficulties and Challenges
Disassembling the Dell Streak 7 can present several challenges. The tight fit of the components and the use of adhesive can make separation difficult. Anticipating these challenges can help mitigate potential issues.
- Adhesive: The back cover and battery may be strongly adhered to the chassis. Applying gentle, even heat (e.g., with a hair dryer on a low setting) can help soften the adhesive and make separation easier. However, excessive heat can damage components.
- Fragile Components: The ribbon cables and connectors are very fragile and can easily be damaged. Use caution and appropriate tools when disconnecting them.
- Small Screws: The screws are small and easily lost. Keep them organized in a container or on a magnetic mat to avoid misplacing them.
Precautions to Avoid Component Damage
Taking the necessary precautions during disassembly is crucial for preserving the integrity of the components. These measures can prevent irreversible damage to the device.
- Use an anti-static wrist strap to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage.
- Work in a clean, well-lit area to avoid dropping small parts.
- Use the correct tools to avoid scratching or damaging components.
- Take photos or videos of each step to help with reassembly.
- Be patient and methodical to avoid rushing and making mistakes.
Component Identification and Functionality
The Dell Streak 7, a pioneering tablet released in 2010, packed a surprising amount of technology into its slim profile. Disassembling the device reveals a fascinating array of components, each playing a crucial role in its operation. Understanding these components and their interactions provides insight into the technological landscape of the early tablet era.
The following sections detail the key components of the Dell Streak 7, their specifications, functionality, and a comparison to similar devices of the time. We will also explore the device’s internal connectivity, illustrating data flow with a schematic diagram.
Key Components and Specifications
The Dell Streak 7’s core components included a Texas Instruments OMAP3630 processor, a significant piece of hardware for its time. This application processor, clocked at 800 MHz, provided the computing power for running the Android operating system and applications. It was complemented by a PowerVR SGX530 graphics processing unit (GPU) responsible for rendering graphics and handling video playback. The device typically came with 512 MB of RAM, a modest amount by today’s standards but sufficient for the applications available in 2010. Storage options usually consisted of 8 GB or 16 GB of internal flash memory. The display was a 5-inch capacitive touchscreen with a resolution of 800 x 480 pixels, offering a decent viewing experience for its era. Other key components included the battery, various sensors (accelerometer, proximity sensor), and the Wi-Fi and cellular radio modules (depending on the model).
Component Comparison with Contemporaries
Compared to other tablets of the same era, such as the Samsung Galaxy Tab or the Apple iPad (original), the Dell Streak 7 held its own in terms of processing power. The OMAP3630 was a competitive processor, offering comparable performance to the processors found in many competing devices. However, the Streak 7’s RAM capacity was often lower than its competitors, potentially leading to slower performance under heavy multitasking. The display resolution, while adequate, was also lower than that of some competitors, resulting in a less sharp image. The design of the Streak 7, with its more elongated aspect ratio, was unique compared to the predominantly square designs of its rivals.
Connectors and Specifications
The Dell Streak 7 utilized a range of connectors for power, data transfer, and audio. The primary connector was a proprietary 30-pin dock connector, similar to those used on some early Apple devices, which provided power and data connectivity. This connector also facilitated connection to accessories such as keyboards and docking stations. A standard 3.5mm headphone jack was included for audio output, and a microUSB port was typically present for data transfer and charging. The specific specifications of these connectors would vary slightly depending on the region and model of the Dell Streak 7. For example, some models may have included a mini-HDMI port for external display output.
Data Flow Diagram
The following simplified flowchart illustrates the data flow within the Dell Streak 7:
[Diagram Description: A rectangular box labeled “User Input” at the top points to a box labeled “Touchscreen Controller.” This connects to a box labeled “OMAP3630 Processor,” which connects to boxes representing “RAM,” “GPU,” “Internal Storage,” and “Wi-Fi/Cellular Modules.” The OMAP3630 also connects to a box labeled “Display Controller,” which leads to the “Display.” Finally, there are lines from the OMAP3630 leading to boxes labeled “Audio Codec” (connecting to the headphone jack) and “USB Controller” (connecting to the microUSB port).]This diagram simplifies the complex interactions within the device, but it highlights the central role of the OMAP3630 processor in managing data flow between input, processing, storage, and output components.
Repair and Maintenance Considerations
Keeping your Dell Streak 7 in tip-top shape requires understanding its common ailments and how to address them. This section details common repair issues, component replacement procedures, and internal cleaning techniques to ensure longevity and optimal performance. Remember, always power down the device completely before undertaking any repair or maintenance.
Common Repair Issues and Solutions
Troubleshooting your Dell Streak 7 starts with identifying the problem. Below is a table categorizing common issues by severity, along with their likely causes and solutions. Remember, attempting repairs yourself voids the warranty, so proceed with caution.
| Problem | Severity | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dead Battery | Moderate | Battery degradation, faulty charging port, or software issues. | Try a different charger. If the problem persists, battery replacement may be necessary. A software reset might also resolve some charging problems. |
| Cracked Screen | Severe | Physical impact or drop. | Screen replacement is required. This is a complex repair best left to professionals due to the delicate nature of the digitizer and LCD. |
| Non-Responsive Touchscreen | Moderate | Software glitch, damaged digitizer, or loose connector. | Try a software reset. If that fails, the digitizer may need replacing. This often requires professional assistance. |
| Slow Performance | Minor | Overloaded memory, outdated software, or numerous background apps. | Close unnecessary apps, perform a software update, and consider a factory reset as a last resort. |
| Overheating | Moderate | Dust accumulation, prolonged use under high load, or faulty internal components. | Clean the device internally (see below). Avoid using the device under direct sunlight or in excessively hot environments. |
Battery Replacement
Replacing the Dell Streak 7’s battery requires careful disassembly. First, power off the device. Then, using a suitable spudger or plastic opening tool, carefully pry open the back cover. Locate the battery connector and disconnect it. Remove the screws securing the battery and carefully lift it out. Install the new battery, ensuring proper alignment, and reconnect the connector. Reassemble the back cover. Remember to use only a Dell-approved replacement battery or one with identical specifications to avoid damaging the device.
Screen Replacement
Replacing the screen is a significantly more complex procedure than battery replacement and should only be attempted by individuals with experience in electronics repair. It requires specialized tools, knowledge of delicate internal components, and a replacement screen assembly. Improper handling can easily damage the digitizer or LCD, leading to further problems. Professional repair is strongly recommended.
Internal Component Cleaning
Dust accumulation inside the device can lead to overheating and malfunctions. To clean the internal components, carefully disassemble the device as described in the disassembly section. Use compressed air to gently blow away dust from the motherboard, battery compartment, and other internal components. Avoid using excessive force or directing the air directly at delicate components. Once cleaned, reassemble the device. Regular cleaning can prevent many issues and prolong the life of your Dell Streak 7.
Comparison with Other Tablets of the Era: Dell Streak 7 Taken Apart Already
The Dell Streak 7, launched in 2010, occupied a unique space in the burgeoning tablet market. Its 7-inch screen size positioned it between the smaller smartphones and the larger tablets emerging at the time. Comparing its internal design and components to competitors reveals a fascinating snapshot of the technological landscape and Dell’s specific design choices.
The Streak 7’s internal architecture, characterized by its Texas Instruments OMAP3630 processor and relatively modest RAM, was typical of mid-range smartphones of the period, rather than the high-end tablets starting to appear. Competitors like the Apple iPad (original model) boasted a significantly more powerful processor and greater RAM, leading to a noticeable performance difference. This choice by Dell likely reflected a strategy to offer a more affordable device, targeting a price-sensitive market segment. However, it also meant compromising on processing power and multitasking capabilities.
Processor and RAM Comparison
The choice of the TI OMAP3630 processor in the Dell Streak 7, while capable, paled in comparison to the Apple A4 processor found in the first-generation iPad. The A4 offered superior processing power and graphics capabilities, resulting in a smoother user experience and better performance in demanding applications. Similarly, the iPad’s RAM allocation was significantly higher, allowing for more efficient multitasking and smoother operation with multiple apps open simultaneously. This difference highlights the disparity in processing power and memory resources between the devices, influencing overall user experience. Other competitors, such as the Samsung Galaxy Tab, also featured more powerful processors than the Streak 7.
Screen Technology and Resolution
The Dell Streak 7 featured a 7-inch capacitive touchscreen with a resolution of 800 x 480 pixels. While this was acceptable for the time, it lagged behind the iPad’s 9.7-inch display with a resolution of 1024 x 768 pixels. The higher resolution and larger screen size of the iPad provided a superior visual experience, particularly for media consumption. This difference underscores the varying approaches to screen technology and the impact on visual quality. The higher pixel density on the iPad resulted in sharper text and images, whereas the Streak 7 offered a less refined viewing experience.
Operating System and Software
The Dell Streak 7 initially shipped with Android 2.2 (Froyo), while the original iPad launched with iOS 4. Both operating systems offered distinct functionalities and user experiences. Android’s open-source nature and customizability appealed to some users, while iOS’s simplicity and user-friendliness were favored by others. The software ecosystems were also different, with varying app availability and functionality. This fundamental difference shaped the overall user experience and the range of applications accessible on each device. The relatively quick updates of iOS, compared to the more fragmented Android ecosystem at the time, also impacted the longevity of software support and feature updates for each device.
Closing Summary
So, there you have it – the Dell Streak 7, dissected and analyzed. More than just a collection of parts, this teardown reveals a fascinating snapshot of mobile technology in its early days. The journey through its innards unveils not only its technical intricacies but also a glimpse into the evolution of tablet design and the challenges faced by manufacturers in those pioneering years. While the Streak 7 may be a relic of the past, its story serves as a valuable reminder of the rapid advancements and constant evolution within the tech world.
 Big Data Solution Big Data Solution
Big Data Solution Big Data Solution